Case A
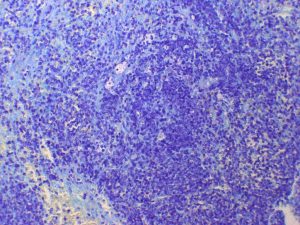
March_07_AAPSP_Proficiency,_canine_spleen_mastocytoma Case A.jpg (114 KB)
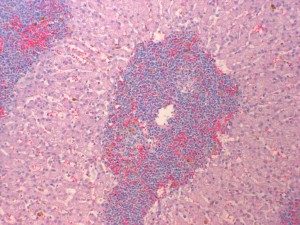
March_07_AAPSP_Proficiency,_canine_spleen_mastocytoma_tol_blue Case A.jpg (114 KB)
History
Enlarged spleen surgically removed from a Greyhound that was showing signs of lethargy and vomition.
Example histopathological description
The section plane of the splenic tissue reveals an intact trabecular stroma, sparse red pulp elements and very few lymphoid elements. Throughout the spleen are irregular clusters of discrete cells displacing the normal cell population and supported by a delicate interstitial stroma. Individual cells have fairly distinct cell borders and polygonal outlines with moderate amounts of eosinophilic cytoplasm showing a finely granular to vacuolated texture.
Diagnosis
Splenic mast cell tumour
Comments
Special stains, such as toluidine blue, giemsa, ZN can be used to confirm the metachromatic nature of mast cell granules. You may wish to consider the following publication which discusses the role of c-kit immunoreactivity correlating this with grading of mast cell tumours – Webster JD and others. Cellular proliferation in canine cutaneous mast cell tumors: Associations with c-KIT and Its Role in Prognostication. Vet Pathol 2007;44:298-308.
Case B
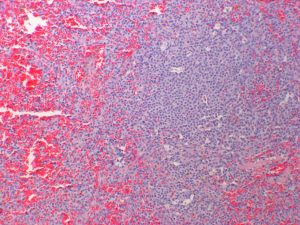
March_07_AAPSP_Proficiency,_canine_liver,_lymphoma case B.jpg (114 KB)
History
Rhodesian ridgeback with hepatomegaly and splenomegaly.
Example histopathological description
In this section of liver, the architecture is distorted due to nodules and connecting streams of infiltrating round cells. Many of these appear to be associated with portal triads, although some central veins are also affected. The capsule is thickened due to infiltrating round cells and there are obvious dilated, and sometimes infiltrated, subcapsular lymphatics. The remaining hepatocytes are vacuolated and there is some evidence of increased cell turnover (some degenerate, some binucleated cells and occasional hepatocytes in mitosis). The infiltrating round cells have vesicular, pleomorphic (round to elongate oval, but some are cerebriform or indented) and variably-sized nuclei. Most nuclei are medium to large when compared to some small lymphocytes and erythrocytes present. The large nuclei often have one or more nucleoli. The cells have small to medium amounts of lightly basophilic cytoplasm. The mitotic rate is about 40 per ten 40X objective fields, indicating a medium mitotic index. There are scattered foci of neutropoiesis and erythropoiesis within the infiltrating round cells and sometimes interspersed amongst hepatocytes. There are scattered megakaryocytes and macrophages containing brown pigment (haemosiderin or lipofuscin?).
Morphological diagnosis
Lymphoma
Comments
In my opinion this was not a high grade lymphoblastic lymphoma or a small cell lymphoma. I thought the cells were intermediate in size, non-cleaved and that the lymphoma was intermediate to high grade. Immunohistochemistry may be used as an aid to defining a prognosis.